Ahoy there.....
As we all know..there are 4 main groups for the human blood...
A
B
AB
O
And for each of these..there's something called the rhesus factor..(which makes it now to 8 subgroups)
A+/-
B+/-
AB+/-
O+/-
Thats right..always remember..even O blood has + or -...keep that in mind..
Now these blood groups are all coded by glycoprotiens(sugars)..protiens..carbohydrates or glycolipids (varying between the blood group types..these substances make up antigens on the surface of the red blood cells (surface antigens)...these are randomly coded by our genetics..and they are permanent for a lifetime..in rare cases such as Demi-Lee Brennan's case is the 1st ever case of blood group change in history...A complete blood type would describe a full set of 30 substances on the surface of Red blood cells..and an individual's blood type is one of the many possible combinations of blood-group antigens..Across the 30 blood groups characterized by the International Society Of Blood Transfusions (ISBT)..over 600 different blood-group antigens have been found..but many of these are very rare and/or are mainly found in certain ethnic groups..these are called special antigens..amongst the common (but still rare) special antigens are...
Kell system
Duffy system
Kid system
I and P systems
Bombay Blood Group
These are classified as special antigens..they are rare and demand specificity for transfusions...
In a Hematology lab..we determine blood groups in order to help us decide what type of blood can be transfused to the patient..for example..an individual with type A+ blood can receive blood from A+ and O+ type only...wrong transfusion will lead to transfusion reaction (a condition where the patient's body starts rejecting the donor's blood)..reason? in the blood plasma..there's ANTIBODIES..antibodies are "gate keepers" that attack anything that doesn't look friendly..including a different subgroup of red cells...below I'll describe each corresponding plasma antibodies in the ABO system..
A: Anti-B antibodies..
B: Anti-A antibodies
AB: NO ANTIBODIES
O : BOTH Anti-A and Anti-B antibodies
Therefore..its always important to perform a cross matching research do determine if the donor's blood is suitable for the recipient..(tomorrow I will enclose a video on how blood typing is done and how cross matching is done)..Also remember..if there is a transfusion reaction EVEN IF THE PROPER ABO BLOOD IS TRANSFUSED TO THE PATIENT..the transfer will be stopped immediately and serology tests would be done to determine special antigens (such as mentioned above)..these are called "warm antibody tests" or "RBC serology tests"..
It is always important that you keep these infos in mind so that in the future you will know what actually is going on when a medical personnel performs blood grouping and talks about blood transfusion reactions to you..So the next time you donate blood or you need a blood transfusion..you'll be aware of the criticality of these tests..hehe..don't underestimate the job of a Scientists..if it isn't because of us..doctors would be facing a hard time making desicions for you..=)
Here I've provided several diagrams related to this post for easier understanding..if there's any questions or corrections to this post..please do inform me in the comment box..I'll answer or edit the post a.s.a.p...
See yea...^_^
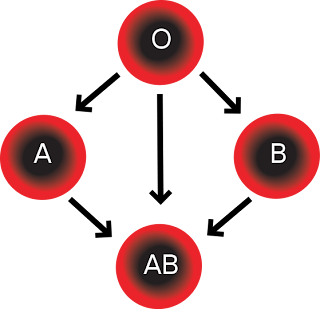
Blood Type Compability
Symptoms Of Hemolytic Reactions (Tranfusion Reactions)

The ABO Blood Group System



